If you want to access the current activity on Android you will need to use the code below:
Microsoft.Maui.ApplicationModel.Platform.CurrentActivity
They made it very easy to access it. Appreciate it!
.NET MAUI, Xamarin.Forms, .NET developer from Hungary
If you want to access the current activity on Android you will need to use the code below:
Microsoft.Maui.ApplicationModel.Platform.CurrentActivity
They made it very easy to access it. Appreciate it!
If you have recently upgraded your XCode version to 14.0, and installed the XCode command line tools too, you will probably notice some error messages when trying to run your Xamarin.Forms, or iOS application from Visual Studio for Mac.
Error MT4109: Failed to compile the generated registrar code.
What actually helped me, is this:
Navigate to https://developer.apple.com/download/all/ and search for Command Line Tools for Xcode 13.4 and Xcode 13.4. Both downloads are big, the XCode itself around 10GB and the CL Tools are around 1GB, so definitely do not do this on metered connections.
Once the downloads are ready, open the XCode.XP file with the Package Archiver, let it extract to downloads, then move it to Applications folder.
After that, install CL tools. Follow the installer’s instructions.
Boom, it’s solved. Issue reported at: https://github.com/xamarin/xamarin-macios/issues/15954
If you need a solution to create multilingual applications without the hassle of implementing all kinds of code, I have good news for you. I’ve migrated my Xamarin.Forms package to .NET MAUI, and you can easily build multilingual applications with MAUI. No need to restart the application, the language takes effect immediately and works on all platforms. You can also use it from XAML, and C# code. It can handle multiple resource files at the same time. It can store the last language set by the user, and the next time you restart it, it will use the same language as the last time the user set it. But instead of letters, watch this video to see what exactly it can do:
This project is available on GitHub: https://github.com/banditoth/MAUI.Packages
To start with, I’ve put together a demo app for you for the sake of demonstration. There is no extra functionality, just 4 buttons. Three of them are to change the language of the application, and one of them is to give us a pop-up window. There is no logic to it yet, but together we will build on the article.
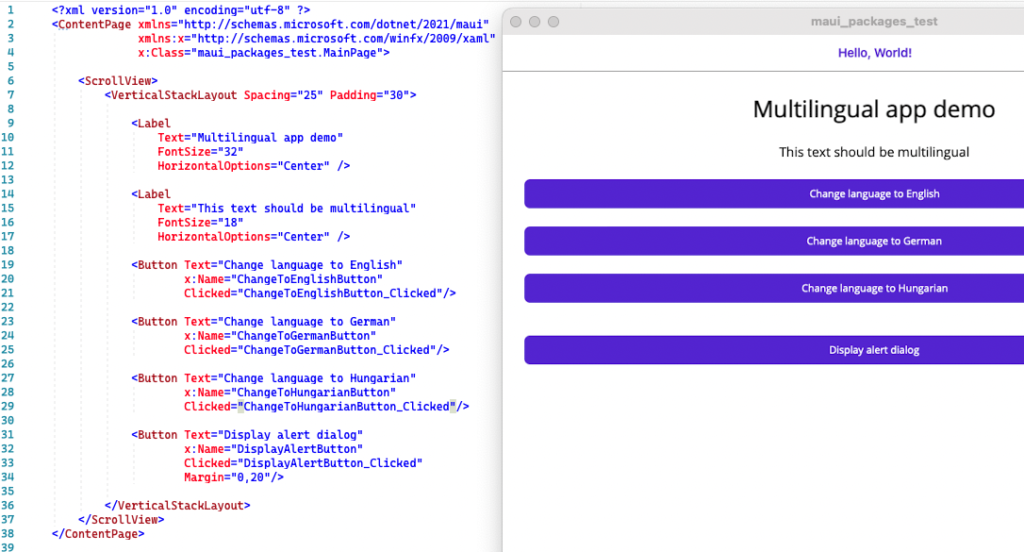
The first thing you will need are files containing multilingual translations. If you are familiar with Xamarin Forms, I will not surprise you: we will use files with RESX extension. By default, all MAUI applications include a directory called Resources. In this directory, I create a directory called Translations next to the Fonts, Images, and Raw directories, where I put the translations used by the application.
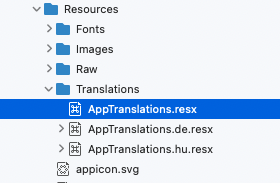
Decide what the default language of your application should be. This is important because the default language is not indicated by a language code at the end of the filename. This language (and file) will be the one that the application will use as fallback, so that if, say, the application can’t find the text in the Hungarian or German translations, it can print it out in that language. In my case, the default language of the application will be English, so I didn’t specify it in the filename.
I’ve created translations for each language with this data:
<data name="WelcomeMessage" xml:space="preserve">
<value>The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog</value>
</data>
<data name="AlertTitle" xml:space="preserve">
<value>Important notice</value>
</data>
<data name="AlertContent" xml:space="preserve">
<value>.NET Bot is cute!</value>
</data>
<data name="AlertConfirm" xml:space="preserve">
<value>Agree</value>
</data>
Since ResX files are set by default to generate a code-behind file from their data, this automatic generation should be disabled for all ResX files other than the default language.
This can be easily done on windows, just click on the file (in this case the German translation) and in the properties window, under Custom tool, clear the ResxFileCodeGenerator value. If you are using Visual Studio on a Mac, you cannot delete this from the interface, so you have to manually remove the option in the project file.
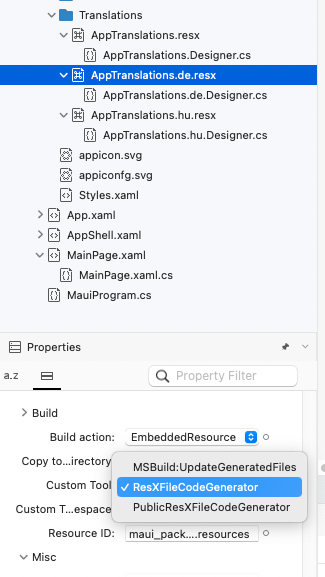
For Visual Studio for mac, find the name of the files containing the translation in the project and delete the following lines:
<Generator>ResXFileCodeGenerator</Generator>
<LastGenOutput>AppTranslations.de.Designer.cs</LastGenOutput>
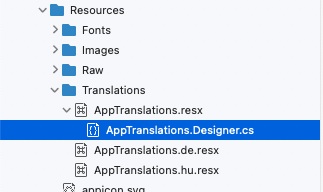
If you did everything right, you will only have these files. If there are any ‘.Designer’ files left in the Solution, feel free to delete them. The important thing is that when you compile the application, they are not recreated by Visual Studio
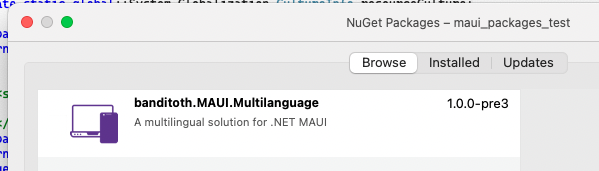
Click on your project with right, then select ‘Manage NuGet Packages’. Search for banditoth.MAUI.Multilanguage in the search bar, and install the result with the exact same name of your search text 🙂 This project is available on GitHub by the way, so if you are experiencing issues with it, you can report over here: https://github.com/banditoth/MAUI.Packages
Let’s navigate to your MauiProgram.cs file, and add some init logic in it!
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Semibold.ttf", "OpenSansSemibold");
})
.ConfigureMultilanguage(config =>
{
// Set the source of the translations
// You can use multiple resource managers by calling UseResource multiple times.
config.UseResource(AppTranslations.ResourceManager);
// If the app is not storing last used culture, this culture will be used by default
config.UseDefaultCulture(new System.Globalization.CultureInfo("en-US"));
// Determines whether the app should store the last used culture
config.StoreLastUsedCulture(true);
// Determines whether the app should throw an exception if a translation is not found.
config.ThrowExceptionIfTranslationNotFound(false);
// You can set custom translation not found text by calling this method
config.SetTranslationNotFoundText("Transl_Not_Found:", appendTranslationKey: true);
});
return builder.Build();
}
In order to use our translations in XAML files, we need to declare the tool’s namespace in XAML. Go to the top of your XAML file, and make the following declaration:
xmlns:multilanguage="clr-namespace:banditoth.MAUI.Multilanguage;assembly=banditoth.MAUI.Multilanguage"
After this declaration you can access the translation tool, so let change this code:
<Label
Text="This text should be multilingual"
FontSize="18"
HorizontalOptions="Center" />
to this:
<Label
Text="{multilanguage:Translation Key=WelcomeMessage}"
FontSize="18"
HorizontalOptions="Center" />
Wherever we need to pass multilingual texts to or from another method, the ITranslator interface comes in handy. This interface is registered in the MAUI ‘s dependency container, so it can be retrieved from the container by constructor injection for example.
private readonly ITranslator translator;
public MainPage(ITranslator translator)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.translator = translator;
}
Unfortunately currently .NET MAUI is not supporting Constructor injection for Shell, but you can request any service from anywhere by adding this little work around to App.xaml.cs (but its definitely not nice):
public App(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
InitializeComponent();
ServiceProvider = serviceProvider;
MainPage = new AppShell();
}
public static IServiceProvider ServiceProvider { get; private set; }
The localized string can be retreived like this (This example shows an Alert dialog for the user in the correct language)
void DisplayAlertButton_Clicked(System.Object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
_ = DisplayAlert(translator.GetTranslation("AlertTitle"),
translator.GetTranslation("AlertContent"),
translator.GetTranslation("AlertConfirm"));
}
To change language, you need to call the SetCurrentCulture method with the desired CultureInfo, like this:
void ChangeToEnglishButton_Clicked(System.Object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
translator.SetCurrentCulture(new CultureInfo("en"));
}
void ChangeToGermanButton_Clicked(System.Object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
translator.SetCurrentCulture(new CultureInfo("de"));
}
void ChangeToHungarianButton_Clicked(System.Object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
translator.SetCurrentCulture(new CultureInfo("hu"));
}
You may have noticed that if you give an image a FontImageSource, the image does not display properly on the UWP platform. This is probably because the default value of the FontImageSource Color property is white, and you probably want to draw it white. Check if you are giving an explicit value to the Color property. If not, try it.
<Image>
<Image.Source>
<FontImageSource
FontFamily="FontIcons"
Color="Black"
Glyph="?"
Size="25" />
</Image.Source>
</Image>
In this article, I would like to share my own experience of how I use different service providers to make sure that my files, music, passwords, emails are available on all my devices. Be it macOS, Windows, Android or iOS. The services detailed below reflect my personal preferences. It is possible that there are better providers that are cheaper or that offer more functionality. If you know of such, help readers by writing in to tell us what works for you. I personally do not like Google’s services. I will not recommend Google Drive, Authenticator and other services in this article, but I am sure that their solutions can solve the architecture I consider to be proven.
What I’d like to show you is how I manage in my daily life to make sure that all my data is in sync and accessible on all my devices, almost without exception.

I personally chose Microsoft’s OneDrive technology as my storage and email provider. They give you 5GB of cloud storage space in their free plan, and an extra 15 GB for emails. For a very long time I subscribed to Microsoft OneDrive +100GB for $2 per month, which is fair, but then recently I decided to subscribe to Microsoft Office 365. Partly so I could have a licensed Microsoft Office subscription of my own to access important files on my personal computer, and partly because they are increasing the cloud storage to 1TB. On top of that, we also get support for recovering our deleted, lost files, or if a file encryption caused by a ransomware virus happens, it can detect and stop the operation. The one terabyte package runs around $60 for a year (+VAT, which is 27% in Hungary). If you buy it, you’ll also no longer have to watch the notifications on the outlook.com web interface. You also get the desktop versions of these in addition to the web versions of Excel, Word, Powerpoint. You can install the desktop version of Microsoft Office on 5 computers with one license key.
OneDrive use pretty serious file encryption, so you can feel safe with your files here, but if you have something really personal in your cloud, there’s the safe feature, which uses an extra encryption algorithm in addition to a number of security requirements
On Windows the OneDrive client is integrated, on macOS it can be installed separately, it integrates quite nicely into the system. You can configure them not to download the entire cloud content to your computer unnecessarily, but to have a file available in the file structure in case you want to store it. What it does is download the file to the physical hard disk before use. This saves a lot of space.
On Android, the OneDrive client also integrates quite well with the operating system, but I don’t use an Android device on a daily basis, just an iPhone.
Mobile clients can automatically back up your camera roll. The upload is an interesting solution for iOS, as they couldn’t do it in the background: they developed a screen called “Night Backup”, which basically layers a wakelock on the display and takes the brightness off the phone. You can view files on your mobile “without downloading”. Handles the web client for the iPhone HEIC format.
Your Outlook email address can be accessed via an Exchange server, which also allows you to save Calendar and Reminders, Notes, Contacts. Personally, I have all syncing turned off in iCloud because I sync my notes to my Outlook account. If you set macOS and iOS to take your outlook email address as your Internet account, the built-in Notes, Email, Calendar app can handle it. This is good because in Windows it’s also built-in to sync everything to the outlook account, so you get a Notepad and Calendar on top of the emails. So if you add a meeting to your calendar, it’ll show up immediately on your iOS/Android device, and also on macOS. Of course it works in all directions. The only downside to the notepad is that on macOS you can’t bold letters, insert a diagram, etc. in the notes app. So if you have an iPad and an Apple Penciled, you’ll have to choose a different way to draw.
Plus one thing besides Outlook that I haven’t seen with any other provider: you can assign aliases to your email address. So you don’t have to register a new email address if you get bored of your old email, you can simply add another address to the account and use up to 10 email addresses with one mailbox.
You can find out more about the packages and their services here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/onedrive/compare-onedrive-plans?activetab=tab%3aprimaryr1
This is probably the subject I have dealt with the least. I spend about 80,000 minutes a year listening to music. I clearly chose an online music service provider. My choice was Spotify. Since then, I have tried a service called Tidal once, which is quasi the same as Spotify, but lossless music, but I didn’t feel it was worth the extra money, I couldn’t take advantage of it.
Spotify has the ability to sync playlists between all platforms. It has a relatively good algorithm for recommending music. You can download tracks of reasonable quality for offline listening on its mobile app. The radio in my car supports it natively. Of course, the 1TB of storage space could hold a lot of music, but you don’t have to worry about downloading it
More information about Spotify: https://www.spotify.com/us/premium/
I never use the same password on any service. In fact, it could be said that I don’t even use passwords, because I don’t know any of them by memory. This is because I let the computer generate super long and complicated passwords. That’s pretty much how to use a password manager effectively, and how to perhaps exist one step more securely on the Internet.
What was important to me was to make the password manager work on macOS and windows, and to be able to add passwords to iOS not only in safari, but also in the apps.
Microsoft Authenticator could have been the perfect solution, but it wasn’t. (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/mobile-authenticator-app) As I am logged in to my work account on my devices, where the password storage functionality of the Authenticator application is disabled by policy, I cannot add passwords to my personal account. But maybe that’s okay, it’s less responsibility on my Microsoft account. After much searching, I found LastPass to be the most sensible password management application. It works on mac on windows, in all browsers, and integrates with iOS. And it can also fill in passwords in apps. https://www.lastpass.com/pricing.
Another very important thing is to protect your account from unauthorised access. Almost all websites can be set up with two-factor authentication, be it Instagram, Facebook, GitHub, etc. Lastpass also has an Authenticator application that can generate such two-factor passcodes. Just like Microsoft authenticator. I’ve set up two-factor authentication everywhere.